Our group of Orthopaedic surgeons provides comprehensive general and sub specialised orthopaedics and trauma service.

Clavicle fractures can occur during sports and falls onto the shoulders. Patients would present with pain and deformity around the collar bone, and usually a deformity of the shoulder.
Diagnosis is confirmed with the help of X-rays. Possible complications include injury to nerves around the shoulder blade and skin problems at the fracture site.
Depending on the severity, clavicle fractures can be treated in an arm sling, or with surgery. Recovery would normally take at least three months depending on the severity of the injury and compliance to therapy.
Minimally invasive clavicle fixture can treat clavicle fracture. The clavicle (collarbone) is the prominent bone on either side at the front of your shoulders and top of chest. A broken collarbone is a very common fracture especially from contact sports.
In general, most orthopaedic specialist can handle a straight forward joint replacement surgery. A complex joint replacement include cases where there is severe deformities, very limited motion or the primary surgery has gone wrong (due to aseptic loosening, poor alignmet or infection).
As modern medicine improves the lifespan for males and females, patients with previous surgeries and implants who need a joint replacement surgery become very challenging as conventional techniques cannot be used.
Dr Chin Pak Lin had been the key person in handling complex and revision joint replacement surgeries formerly at SGH.
 The rotator cuff muscles surround and move the shoulder joint, a tear in the muscle will cause pain and weakness in the shoulder.
The rotator cuff muscles surround and move the shoulder joint, a tear in the muscle will cause pain and weakness in the shoulder.
Repair of the torn rotator cuff can now be done using keyhole technique with faster recovery, less pain and nicer cosmetic results.
Dr Tan Chyn Hong has even discovered the technique of keyhole rotator cuff repair without using any suture anchors, eliminating the use of any metal, plastic or biodegradable materials.
 A shoulder dislocation can result in persistent instability with subsequent multiple dislocations. The shoulder can be stabilized using keyhole technique. This procedure is known as arthroscopic bankart repair. Dr Tan Chyn Hong employs a novel technique that requires only 2 incisions instead of the usual 3 incisions. This new technique is less damaging to surrounding tissues and achieves better cosmetic result.
A shoulder dislocation can result in persistent instability with subsequent multiple dislocations. The shoulder can be stabilized using keyhole technique. This procedure is known as arthroscopic bankart repair. Dr Tan Chyn Hong employs a novel technique that requires only 2 incisions instead of the usual 3 incisions. This new technique is less damaging to surrounding tissues and achieves better cosmetic result.
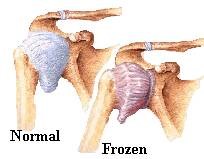 Frozen shoulder or adhesive capsulitis is a disorder in which the capsule ( connective tissue surrounding the shoulder joint) becomes inflamed and stiff. The patient presents with restriction in shoulder movements and chronic pain. The symptoms can last up to 2 years or more without treatment. The exact cause of the condition is unknown but there is an association with diabetes, stroke and trauma/injury. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory medications, physiotherapy, manipulation under general anaesthesia and keyhole ( arthroscopic) release of the tight capsule.
Frozen shoulder or adhesive capsulitis is a disorder in which the capsule ( connective tissue surrounding the shoulder joint) becomes inflamed and stiff. The patient presents with restriction in shoulder movements and chronic pain. The symptoms can last up to 2 years or more without treatment. The exact cause of the condition is unknown but there is an association with diabetes, stroke and trauma/injury. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory medications, physiotherapy, manipulation under general anaesthesia and keyhole ( arthroscopic) release of the tight capsule.
Shoulder joint arthritis is a disorder characterised by pain and stiffness. It can be caused by injury, overuse or unrepaired rotator cuff tears. The cartilage in the joint is worn out and extra bone spurs start to form. Treatment involves medication, physiotherapy, injections into the joint and joint replacement. Joint replacement involves removing the worn out joint surfaces and replacing them with metal and plastic components. After a joint replacement, patient will experience greater range of motion and less pain, improving the overall function of the shoulder.

In general, most orthopaedic specialist can handle a straight forward joint replacement surgery. A complex joint replacement include cases where there is severe deformities, very limited motion or the primary surgery has gone wrong (due to aseptic loosening, poor alignmet or infection).
As modern medicine improves the lifespan for males and females, patients with previous surgeries and implants who need a joint replacement surgery become very challenging as conventional techniques cannot be used.
Dr Chin Pak Lin had been the key person in handling complex and revision joint replacement surgeries formerly at SGH.
Elbow joint arthritis is a disorder characterised by pain and stiffness. It can be caused by injury or overuse. The cartilage in the joint is worn out and extra bone spurs and loose bodies start to form. Treatment involves medication, physiotherapy, arthroscopic washout and joint replacement. Joint replacement involves removing the worn out joint surfaces and replacing them with metal and plastic components. After an elbow joint replacement, patient will experience greater range of motion and less pain, improving the overall function of the shoulder.
Elbow arthroscopy (keyhole surgery) is a specialised procedure. One of the commonest indications for elbow arthroscopy is arthritis with loose bodies "jamming" the joint and causing a painful locking sensation. The procedure removes the loose bodies, extra bone spurs and tight capsule to achieve greater range of motion and substantial pain relief. The advantages of keyhole surgery includes less pain, faster recovery and nicer cosmetic result.
 Why Hip Replacement
Why Hip ReplacementIf you are experiencing such symptoms, you might require to undergo a hip replacement surgery
In hip replacement surgery, an artificial prosthesis is surgically implanted to replace the function of the diseased hip joint. Highly effective surgery with a reported 90% satisfaction rate with the durability of about 20 years.
Novel advances:Hip fracture commonly occurs in elderly patients with osteoporotic bones when they suffer a fall or direct impact to the side of the hip. While some elderly people have other possible health issues that make them more likely to trip and fall. It is a serious and possibly life-threatening injury that requires immediate medical attention. As a result, most hip fractures require surgery other than for those who are too ill to undergo any form of anaesthesia or are bedridden. The type of surgery used depends on the location and severity of your hip fracture, as well as your health condition:
In general, most orthopaedic specialist can handle a straight forward joint replacement surgery. A complex joint replacement include cases where there is severe deformities, very limited motion or the primary surgery has gone wrong (due to aseptic loosening, poor alignmet or infection).
As modern medicine improves the lifespan for males and females, patients with previous surgeries and implants who need a joint replacement surgery become very challenging as conventional techniques cannot be used.
Dr Chin Pak Lin had been the key person in handling complex and revision joint replacement surgeries formerly at SGH.
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure where a camera and working portal is inserted into the hip joint to treat problems like:
Injection into the hip joint under x-ray guidance. As the joint is deep seated, patients need to be sedated for the procedure. It serves as as a diagnostic test or therapeutic procedure. In general there are two types of injections:
Meniscus tear is a very common knee injury. The meniscus is a rubbery, C-shaped disc found in your knee that behaves like a cushion between your shinbone and your thighbone. There are two menisci in each knee to keep your knee steady by balancing your weight across the knee.
A meniscus tear is usually caused by sudden and forced twisting or turning of the knee when it is bent. People who often play sports or lift heavy objects are at higher risk of meniscus tear.
The RICE treatment (Rest, Ice, Compress, Elevate) and ample rest is sometimes enough to relieve the pain and give the meniscus tear to heal on its own. Some cases may however require surgical treatment like the knee arthroscopy.
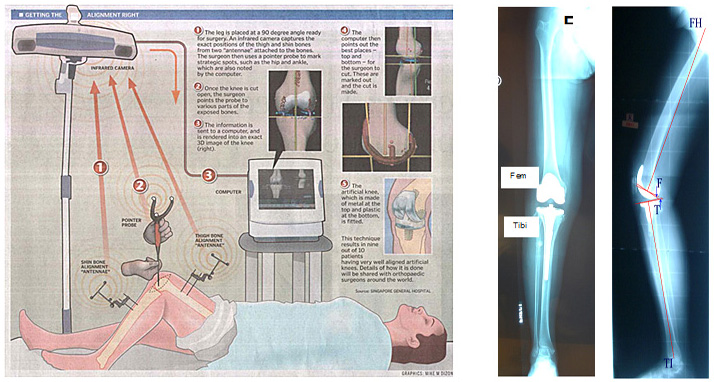
Conventional knee joint replacement technique uses alignment rods to guide surgeon in the bone cuts. However, the outcome heavily depends on the surgeon's experience and patient's conditions like density of soft bones (osteoporosis) - leading to a less than ideal outcome. In computer-assisted and robotic surgery, the computer is like a GPS allowing the surgeon to be able to rehearse and adjust for the best outcome.
Currently, there are only two dedicated orthopaedic robotic systems for the replacement surgery.
This is a haptic robotic arm where the surgeon guides the arm during the surgery. The current software only allow for acetabular milling for hip replacement surgery and partial/unicondylar knee replacement surgery. The total knee replacement platform will be starting beta testing soon.
The Robodoc system is not a novel technique. More than 30,000 total knee replacement surgeries have been performed successfully. Dr Chin Pak Lin started the robotic knee program on 16 May 2012. To date, about 60 such surgeries have been successfully performed, audited and followed-up. This robotic arm is an active robot where the surgeon merely coaches the arm while it performs all the work. It is very different from the MAKOplasty platform as this is is an open platform where both unicondylar and total knee replacement surgeries can be performed.
In general, most orthopaedic specialist can handle a straight forward joint replacement surgery. A complex joint replacement include cases where there is severe deformities, very limited motion or the primary surgery has gone wrong (due to aseptic loosening, poor alignmet or infection).
As modern medicine improves the lifespan for males and females, patients with previous surgeries and implants who need a joint replacement surgery become very challenging as conventional techniques cannot be used.
Dr Chin Pak Lin had been the key person in handling complex and revision joint replacement surgeries formerly at SGH.
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure where a camera and working portal/s are placed through tiny incisions to visualize the knee. Multiple types of therapeutic procedures can be carried out:
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is a major stabilizing ligament of the knee. ACL injury is one of the commonest knee injury and ACL reconstruction is one of the commonest surgery done. The ACL reconstruction can be done using keyhole technique. Newer advances involve using special techniques to:
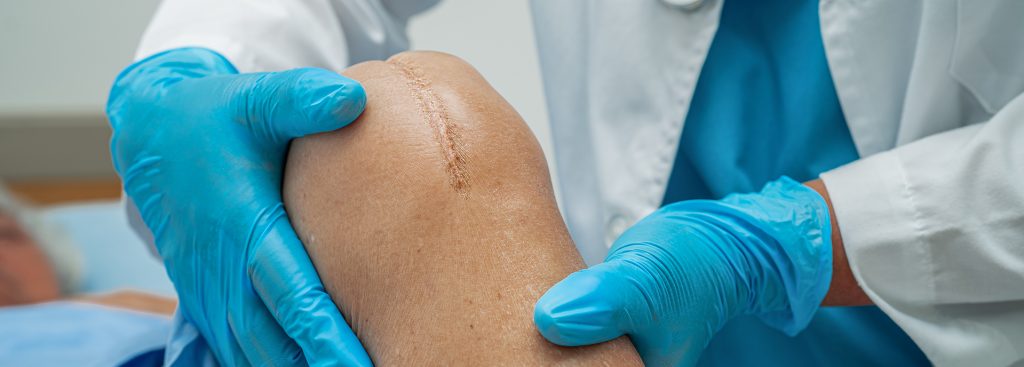
Throughout total knee replacement surgery, an artificial prosthesis is surgically implanted to take over the function of the disease knee joint. Indications of knee joint replacement surgery are severe pain with loss of function. Very effective surgery with a reported 90% satisfaction rate lasting about 20 years.
Novel advances:Newer techniques include using PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) combined with the aforementioned injections.
The nerves in the spine in the neck region (cervical spine) may be compressed by various disease conditions. This may result in pain, numbness and weakness of the arms and legs. For compression at one or two spinal levels (rarely three or more), Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion is a surgery that may be performed.
The spine is approached from the front of the neck, utilising a safe “window” between the vital structures of the neck. This approach has been safely used for more than 60 years. At the spine, the discs and structures compressing the nerves are removed under the operating microscope. After decompression of the nerves, the gaps in the discs and bones are reconstructed with bone graft or synthetic spacers. In addition, a titanium plate and screws are inserted in the adjacent bone to stabilise the spine. The locking of the two bones across a disc/joint is called fusion.
The recovery from Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion is relatively quick. Most patients stay only one or two days in the hospital and no external brace is usually necessary. The success rate of this surgery is usually high (more than 90% of patients experience improvement in their symptoms).
The spinal cord is an important nerve structure that is normally protected by the bones of the spine. Loss of spinal cord function occurs when it is compressed by various diseases. One common condition is the compression of the spinal cord by degenerative changes of the spine in the neck such as enlarged joints, thickened ligaments, “bone spurs” and disc protrusions. This can result in progressive disability and loss of function (cervical myelopathy), including clumsiness of hands and inability to walk. This usually occurs in older patients.
Cervical laminoplasty is a type of surgery that is often used to treat this condition. In this surgery, the spine is approached from the back. The back part of the spine (lamina) is “reshaped” with special instruments to create more space for the spinal cord. This relieves the compression on the spinal cord.
Multiple levels of compression (usually more than 3) can be safely treated at the same time with cervical laminoplasty. The main aim of the surgery is to stop the deterioration of spinal cord dysfunction although a significant number of patients do experience improvement, especially if surgery is performed soon after the onset of symptoms.
While Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) is an effective and reliable surgery to treat conditions of the cervical spine, there is some concern over the reduced flexibility of the neck joints after surgery. This may result in earlier degeneration of the joints in the spine next to the fused level.
Cervical Disc Replacement (Arthroplasty) may be suitable for some patients instead. An “artificial disc” is used in the reconstruction of the cervical spine. The “artificial disc” is usually made of metal, ceramic and/or plastic. It acts as a spacer while allowing the joints of the spine to continue to move after surgery.
Current studies show that the results of the Cervical Disc Replacement with an “artificial disc” are equivalent to those of ACDF. It has not been proven to reduce degeneration of the joints in the spine next to the operated level. The actual longevity of such implants is currently unknown though most of the established models have at least 3 to 10 years of follow-up history.
As a person ages, the joints and discs of the spine degenerate. As part of the degeneration process, the joints and ligaments of the spine can enlarge and thicken. This sometimes leads to compression of the spinal nerves. Surgery may be required to relieve the nerve compression when it causes nerve dysfunction (such as pain, weakness, numbness and difficulty with prolonged standing or walking).
In Minimally Invasive Laminotomy or Laminectomy, the surgeon uses one or more small incisions and special retractors to visualise the compression area under the operating microscope. He then removes the abnormal structures compressing on the spinal nerves. Patients are usually able to go home within 1-2 days after the surgery.
Traditional open spine surgery involves cutting and pulling the back muscles out of the way so as to expose the spine before actual surgery is performed. This is necessary in order to see the area of the spine that needs to be operated on. Sometimes more muscle is cut so that the surgeon can see the area better, especially in deeper areas. Injury to the muscles can be significant. While they usually recover, this can take a long time and causes a lot of pain as well as loss of function in the meantime. Additionally when muscle injury is severe the body repairs with scar tissue instead of muscle tissue. The function of that particular muscle may risk being lost permanently.
Minimally invasive spine surgery modifies the approach to the spine by reducing the trauma to the back muscles, while still allowing the surgeon to see and access the area of the spine that requires surgery. This is achieved with special access retractors, x-ray imaging and guidance equipment. Several small incisions are made instead of a large one, sparing all the muscles in between. With special retractors, the same size incisions are made whether the area to be operated on is deep or superficial.
The advantages of minimally invasive spine surgery are:
The long term effectiveness of the minimally invasive spine surgery is the same as the traditional approach. However the spine surgeon needs to undergo special training in order to perform the surgery well. In addition, the equipment is more expensive compared to traditional surgery and the approach cannot be applied to certain areas of the spine.
Sometimes the ring (annulus) around a spinal disc ruptures and part of the core (nucleus) protrudes out of the ring. This is a “slipped disc” (prolapsed intervertebral disc or herniated nucleus pulposus). The protruded disc fragments can compress on the spinal nerves causing pain, weakness and numbness. This may be treated with surgery if conservative treatment fails or if symptoms are severe, threatening nerve damage.
Minimally invasive lumbar microdiscectomy is a more advanced approach of performing surgery to treat this condition. Under X ray guidance a small incision is made over the back. Special retractors are inserted to approach the spine. Under the operating microscope, a small area of bone and ligament at the back of the spine is removed. The spinal nerves are identified and protected. The prolapsed disc fragments are then removed with fine instruments. Patients are usually able to go home within 24 hours after the lumbar microdiscectomy surgery.
Performed under X-ray guidance, spinal injections can be used for diagnosis of pain source or treatment for pain relief.
For pain relief, spinal injections can be more effective than an oral medication in delivering medication directly to the source or location of the pain. The duration of back pain relief provided depends on the type of spinal injection. The most common epidural steroid injection is used in temporarily relieving lower back pain especially for people who experience episodic severe back pain.
For diagnosis of pain, spinal injections (together with physical and other imaging examinations) can help in developing further treatment for the patient.
In persons with osteoporosis, the bones become weaker and can break or fracture with minor or even no trauma. One common area where fractures occur is the spine and a common fracture that occurs is a compression fracture. In a spine compression fracture, a bone in the spine (vertebra) fractures and becomes flattened.
Sometimes the fracture does not heal or takes too long to heal causing prolonged pain, disability and deformity. When this happens, the patient, who is usually an elderly person, is unable to get out of bed and be mobile due to pain. This can lead to many complications such pressure sores, lung and urinary tract infections.
Vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty is the surgery performed to relieve the patient's pain from the spine fracture. In the surgery, bone cement is injected into the fractured vertebra through 2 small puncture wounds. This stabilises the fracture and reduces pain significantly, allowing the patient a quick return to function. The difference between vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty is that in the latter, a balloon is used to “jack” the fractured parts of the vertebra apart before injecting the cement thus restoring, at least partially if not completely, the original shape of the vertebra.
When one has an injury and suffers a cut or a bruise, the body cells will heal and regenerate. However, cartilage has a limited regenerative ability once it has been damaged. This can cause tissue damage with a residual defect to the area. This usually leads to swelling, constant pain, and limited mobility.
The ankle joint has been found to have the highest occurrence of cartilage injury (osteochondral lesions). They are always neglected when it has not been diagnosed previously and not commonly understood what can be done to deal with this problem.
For one with a serious ankle injury, one may require ankle cartilage regeneration. Dr David Su has been an early adopter in Singapore in using tissue scaffolds in cartilage regeneration in the ankle joint. Dr Su uses tissue scaffolds, and plenty of patients have recovered and resumed sports after a period of rehabilitation.
As an orthopaedic surgeon and foot and ankle sub-specialist, Dr David Su has the specific knowledge and experience to help patients suffering from problems in this area, leading them on the route to recovery.
Ankle fractures can occur as a result of twisting injuries to the ankle region during sports or sustained due to falls from heights. They can also occur with less trauma if the patient has a background of osteoporosis.
Patients would present with pain and swelling around the ankle and have difficulty weight-bearing.
Diagnosis is confirmed with the help of X-rays, and sometimes CT scan is required to further delineate injury in complex ankle fractures. Delayed diagnosis can result in a more complex surgery if surgery is required, longer healing time and arthritis in the long run.
Not all ankle fractures require surgery. If the fracture is stable, and the joint is intact, the fracture may be treated in a cast. Recovery from an ankle fracture depends on the severity of the fracture, however, most patients should expect at least three months of relying either on crutches or walking aid.
Foot drop refers to the difficulty of lifting the front part of the foot. It occurs when the muscles and tendons pulling the foot up are unable to function. If you have foot drop, you will have difficulty walking as your foot or toes are constantly dragging on the ground.
Tendon transfer may be used to treat foot drop when wearing a brace or physical therapy is not a viable option. It is a procedure in which a functioning tendon and its muscles is taken from another part of the foot to replace the one from the drop foot.
Complications from diabetes include nerve damage and poor blood circulation. These complications can lead to development of foot sores and ulcers that are difficult to treat. It is important to have proper diabetes management and foot care in preventing diabetes amputation of the foot. The Orthopaedic Centre provides foot care management and diabetes amputation prevention services.
In general, most orthopaedic specialist can handle a straight forward joint replacement surgery. A complex joint replacement include cases where there is severe deformities, very limited motion or the primary surgery has gone wrong (due to aseptic loosening, poor alignmet or infection).
As modern medicine improves the lifespan for males and females, patients with previous surgeries and implants who need a joint replacement surgery become very challenging as conventional techniques cannot be used.
Dr Chin Pak Lin had been the key person in handling complex and revision joint replacement surgeries formerly at SGH.
Bunions are a common problem which are often hereditary and exacerbated by footwear. The standard of care for painful bunions is now the scarf osteotomy. The scarf osteotomy ensures removal of the bunion, shifting the bones back to an optimal position and gives good outcomes. Patients are allowed to walk with protective foot wear in the immediate post-operative period. Many are usually very pleasantly surprised at the lack of discomfort.
Dr David Su has found that many patients have avoided addressing painful foot deformity as they have been misinformed that bunions recur after bunion surgery, resulting in needless suffering. With the scarf osteotomy, there is a very low recurrence rate. Patients are encouraged to return to sporting activity.
The foot and ankle is the commonest injured joint in sports. Whilst most patients who suffer ankle sprains recover spontaneously, some do not. More severe sprains result in chronic ankle instability and limitations in functions of daily living and sporting activity. There is potential risk of further damage to the joint once the biomechanics has been altered.
Ankle ligament reconstruction is performed to address ankle instability. With a short period of immobilisation and rehabilitation, patients are encouraged to return to sporting activity.
Minimally invasive surgery is performed to allow a faster recovery and shortened hospital stay. Ankle arthroscopy (putting a small camera into the ankle joint) is one such example. It is performed to address problems of chronic ankle pain resulting from impingement in the ankle joint.
Dr David Su, being an orthopaedic surgeon who is fellowship-trained in foot and ankle surgery, will be best able to address your concerns of foot and ankle problems
Flat feet (pes planus) sometimes causes pain due to stretching of ligaments & tendons or bony impingement due to the abnormal structure of the foot. If left unaddressed, some cases progress to arthritis of the midfoot and ankle joints.
Correction of this deformity may involve flat foot surgery where there are tendon transfers or bony procedures which are decided based on an individualised clinical assessment.
Carpal tunnel syndrome causes numbness, tingling, weakness and other problems in the hand and arm. It occurs due to the pressure on the median nerve that runs from the forearm through the carpal tunnel to the hand. This pressure can come from swelling or anything that makes the carpal tunnel smaller.
Early diagnosis and treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is important to prevent long-term damage to the median nerve. Surgery may not be needed if the condition is diagnosed early and can be treated with just splints and medications. However, carpal tunnel surgery is needed if the symptoms persist or are severe even after nonsurgical treatment.
Ganglion cyst is a benign lump or swelling that commonly develops on the joints of the wrist or hand. It is filled with jelly-like fluid similar to those that lubricates joints and varies in sizes.
Ganglion cyst is harmless and requires no medical treatment. It will disappear by itself. However if your ganglion cyst is causing severe pain and other problems to you, please seek medical attention from The Orthopaedic Centre and our doctors will advise you on cyst removal or the most appropriate treatment.
Hand and wrist fractures most commonly occurs during a fall when people land hard on an outstretched hand while trying to catch themselves. More severe fractures may occur in more forceful impacts, such as a car accident or a falling off a ladder. Osteoporosis, a condition in which the bone becomes very weak and brittle, may increase the likelihood of hand and wrist fractures from a simple fall.
It is important to treat hand and wrist fractures as soon as possible. The bones in the hand are aligned precisely to allow you to perform many everyday functions like grasping a pen or buttoning a shirt. If the fracture is not properly treated, the bones may not heal in proper alignment and can affect your ability to perform the everyday functions.
The type of treatment used for hand and wrist fractures depend on various factors like your age, level of activity, severity of injury and presence of arthritis. Only a splint or cast may be needed for fractures that are not displaced or have been aligned. Surgery may be needed for fractures that need bone alignment and/or stabilization.